STAT3 Target Analysis Report Summary


About the Target
Based on the provided information, here are key viewpoints about the role of STAT3:
STAT3 is a signaling protein involved in the regulation of gene transcription. It is activated by phosphorylation and forms dimers that translocate into the nucleus to activate target genes [1].
miRNAs play a critical role in regulating STAT3 in various types of human cancers [1].
The inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway can lead to the inhibition of tumor growth, invasion, and induction of cancer cell apoptosis [2].
Notch pathway and inflammatory elements interact with STAT3 to promote breast cancer progression [3].
IL-18 can influence colitis by regulating the function of goblet cells through the IL-22/STAT3 signaling pathway [4].
DNA methylation, regulated by inflammatory cytokines, can affect the transformation of inflammation into colorectal cancer by modulating STAT3/NF-kappaB signaling [5].
Overall, STAT3 is a key factor in cancer progression, and its regulation and interactions with other proteins and pathways play a crucial role in various cancer types.
STAT3, also known as mitoSTAT3, plays a critical role in various cellular processes and signaling pathways. Upon initial stimulation, mitoSTAT3 undergoes posttranslational modifications, leading to its association with mitochondrial proteases and subsequent proteolytic cleavage. Proteolytic fragments of mitoSTAT3 may potentially contribute to extramitochondrial signaling [6].
Further research reveals that the activation of STAT3 promotes the transcription of miR-384 and Rorgammat (RORC), which are involved in Th17 cell polarization [7]. Additionally, SUMOylation and SENP3 are implicated in the regulation of STAT3 activation, particularly in basal and stressed microenvironments affected by cigarette components and excessive IL-6 [8].
In the context of cancer immunity, STAT3 phosphorylation in cancer cells facilitates interactions between immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, promoting tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. STAT3 also regulates the expression of immune checkpoint molecule PD-L1, which has downstream effects on immune checkpoint regulation [9].
Moreover, a new protein loop involving STAT3/SHMT2/PKM2, rather than the previously known STAT3/HIF-1alpha/PKM2 loop, can be active under inflammatory conditions. This alternate loop contributes to metabolic shifts and oxidative stress, ultimately leading to stabilized anaerobic glycolysis [10].
In summary, STAT3 is involved in various cellular processes such as mitochondrial stability, Th17 cell polarization, regulation of immune checkpoints, and metabolic shifts under inflammatory conditions. Its activation and modulation play pivotal roles in both normal cellular functions and pathological processes such as cancer.
Figure [1]
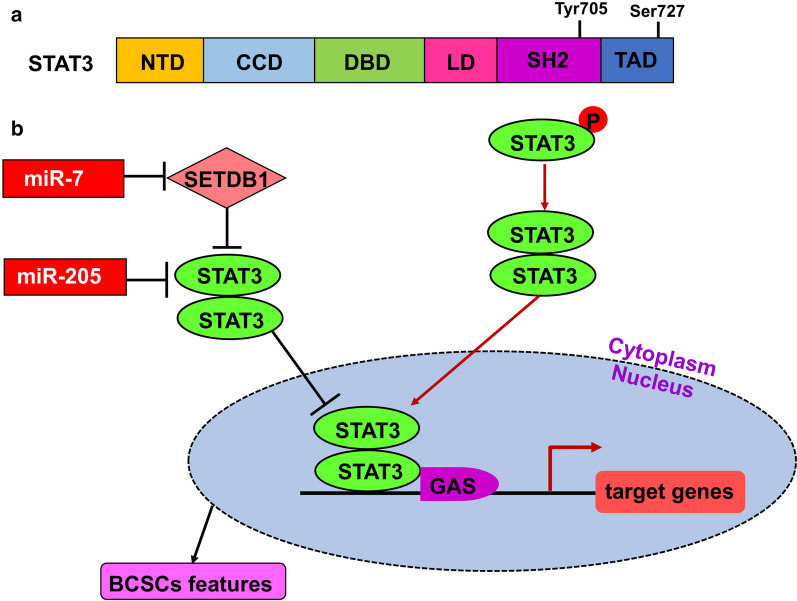
Figure [2]
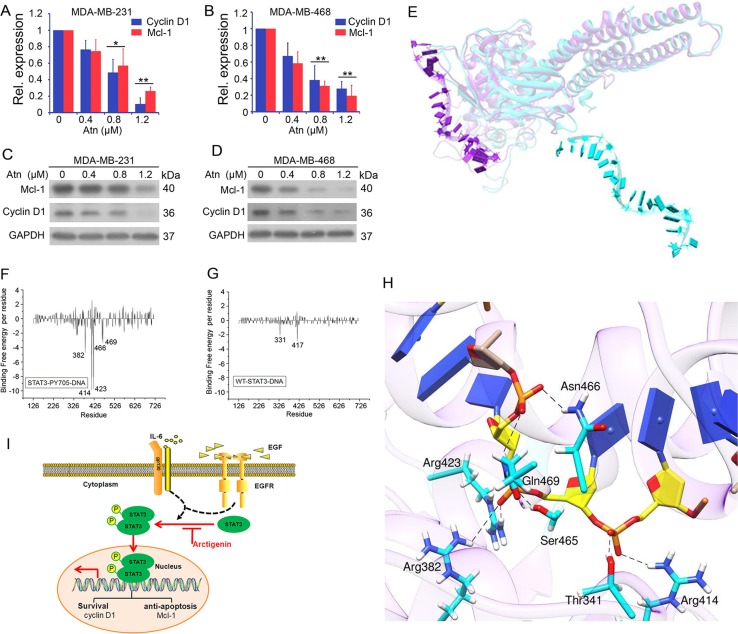
Figure [3]

Figure [4]
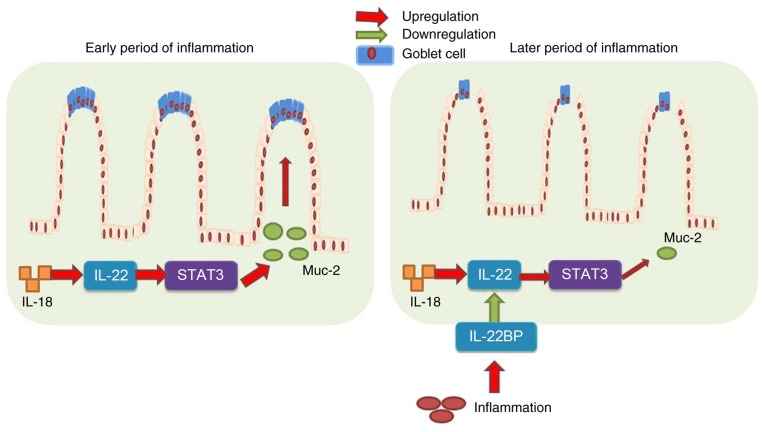
Figure [5]

Figure [6]
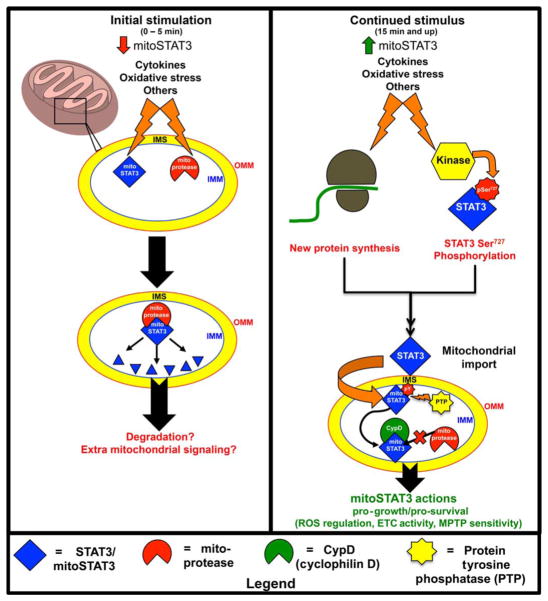
Figure [7]
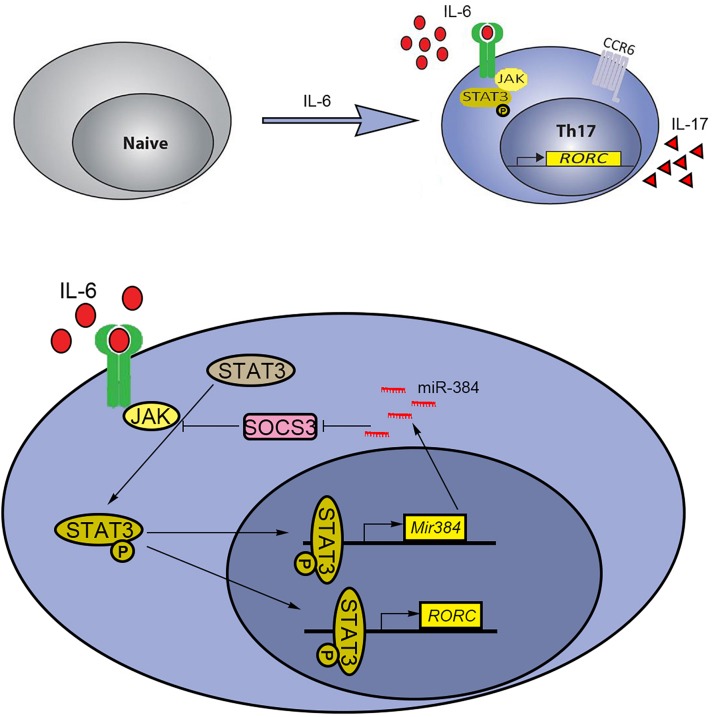
Figure [8]
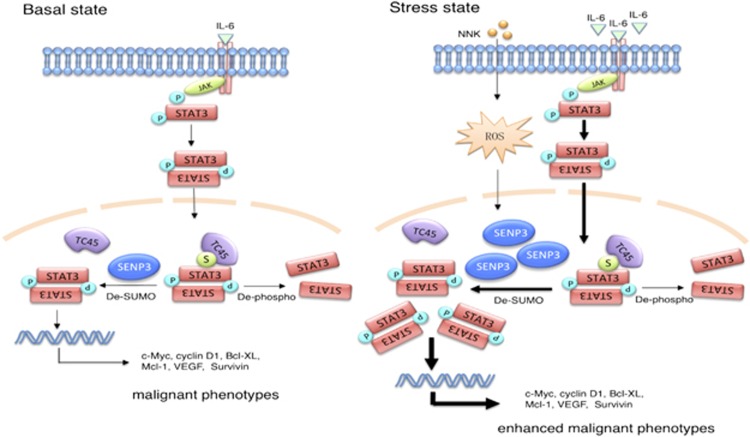
Figure [9]
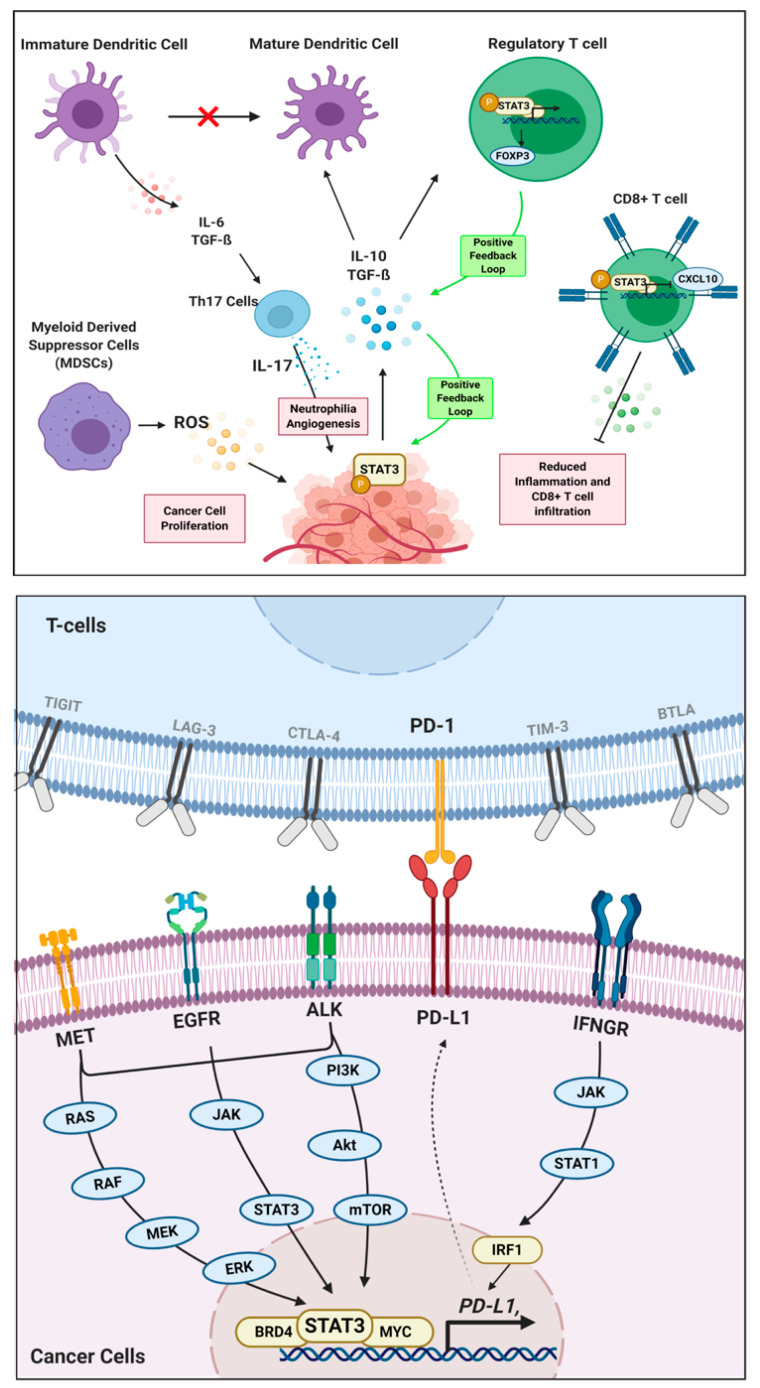
Figure [10]

Note: If you are interested in the full version of this target analysis report, or if you'd like to learn how our AI-powered BDE-Chem can design therapeutic molecules to interact with the STAT3 target at a cost 90% lower than traditional approaches, please feel free to contact us at BD@silexon.ai.
More Common Targets
ABCB1 | ABCG2 | ACE2 | AHR | AKT1 | ALK | AR | ATM | BAX | BCL2 | BCL2L1 | BECN1 | BRAF | BRCA1 | CAMP | CASP3 | CASP9 | CCL5 | CCND1 | CD274 | CD4 | CD8A | CDH1 | CDKN1A | CDKN2A | CREB1 | CXCL8 | CXCR4 | DNMT1 | EGF | EGFR | EP300 | ERBB2 | EREG | ESR1 | EZH2 | FN1 | FOXO3 | HDAC9 | HGF | HMGB1 | HSP90AA1 | HSPA4 | HSPA5 | IDO1 | IFNA1 | IGF1 | IGF1R | IL17A | IL6 | INS | JUN | KRAS | MAPK1 | MAPK14 | MAPK3 | MAPK8 | MAPT | MCL1 | MDM2 | MET | MMP9 | MTOR | MYC | NFE2L2 | NLRP3 | NOTCH1 | PARP1 | PCNA | PDCD1 | PLK1 | PRKAA1 | PRKAA2 | PTEN | PTGS2 | PTK2 | RELA | SIRT1 | SLTM | SMAD4 | SOD1 | SQSTM1 | SRC | STAT1 | STAT3 | STAT5A | TAK1 | TERT | TLR4 | TNF | TP53 | TXN | VEGFA | YAP1

