CASP3 Target Analysis Report Summary


About the Target
Based on the given context information, the following key viewpoints can be extracted regarding the role and regulation of caspase-3 (CASP3):
In corals, CASP3 is activated by an unknown sensor and pathway during invasive infection, leading to the cleavage of gasdermin E (GSDME) and subsequent induction of pyroptosis [1A].
In cancer cells, increased levels of prostate cancer antigen 3 (PC-3) can perturb zinc regulation, potentially altering basal caspase-3 activity within the cell [2].
During apoptosis, activated caspase-3 cleaves a small percentage of p65, generating a p65 fragment that interferes with the activation-induced nuclear translocation of RPS3. This selective inhibition of NF-kappaB anti-apoptotic transcription shifts the cellular balance towards apoptosis [3].
The expression of pUL138 in gastric cancer cells can inhibit caspase-3 cleavage and block the function of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), thereby promoting apoptotic cancer cell death [4].
Caspase-3 activation is involved in the Phoenix Rising pathway, where it promotes programmed cell death by apoptosis and leads to the production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), which accelerates tumor repopulation [5A].
Caspase-3 activation is also linked to the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway, where it plays a role in determining cell fate in response to DNA damage caused by radiation [5B].
These viewpoints provide insights into the diverse roles and regulatory mechanisms of caspase-3 in various biological contexts, including coral infection, cancer progression, apoptosis, and DNA damage response.
Caspase-3, also known as caspase-3/-7, is a key protein involved in the apoptotic signaling pathway in different cell types. In Jurkat T cells, MST1 acts as a regulator of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, and its proteolytic activation is stimulated by active ERK1/2 signaling. Caspase-8 may potentially activate MST1 in these cells, and MST1, in turn, potentiates the activation of caspase-3, -7, and -8, forming a positive feed-back loop to amplify the apoptotic signal [6].
In gastric cancer (GC) cells, MeCP2 inhibits apoptosis by suppressing the MYOD1/Caspase-3 signaling pathway. Knockdown of MeCP2 leads to increased expression of MYOD1 and results in the up-regulation of active Caspase-3, inducing apoptosis and inhibiting GC cell proliferation [7].
TFF3, when overexpressed, activates the PI3K/AKT pathway to block the mitochondria-induced apoptotic pathway in prostate tumorigenesis. Silencing TFF3 has the opposite effect, promoting the release of proapoptotic proteins from the mitochondria, activating caspase-9 and caspase-3, and inducing apoptotic cell death [8].
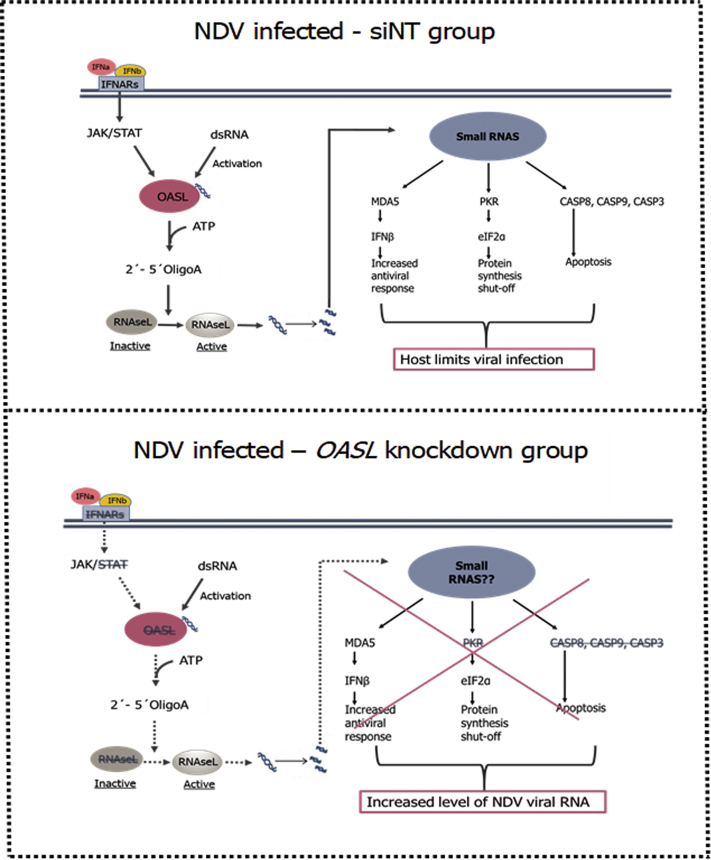
During Newcastle disease virus (NDV) infection in a chicken fibroblast cell line, knockdown of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-like (OASL) leads to lower expression of CASP3 gene and other caspase genes. This reduction in caspase expression results in a higher level of NDV viral RNA [9].
Overall, caspase-3 plays a crucial role in apoptosis regulation in different cellular contexts, either as a positive regulator in the apoptotic pathway or as a target for inhibition by specific proteins. Its involvement is observed in T cells, gastric cancer cells, prostate tumorigenesis, and NDV infection.
Figure [1]
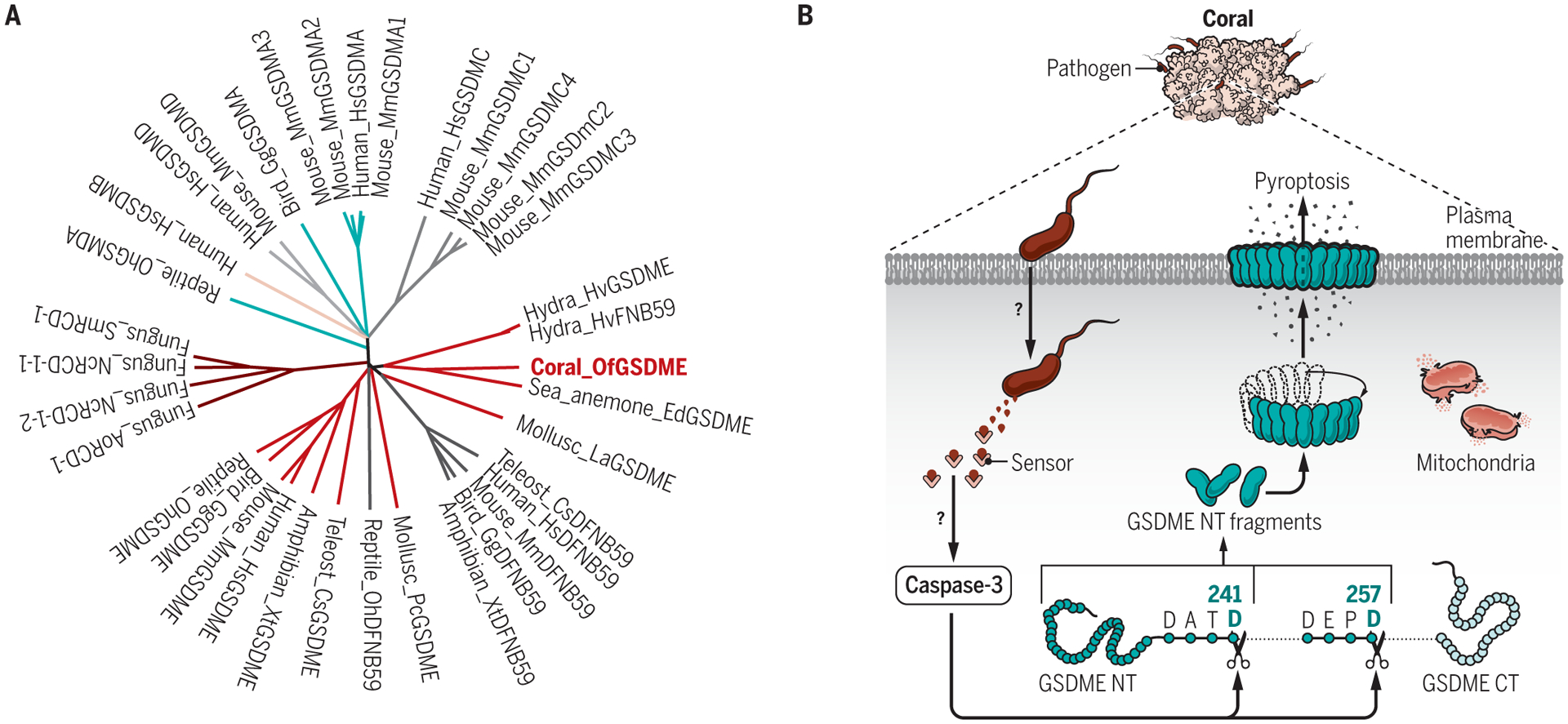
Figure [2]
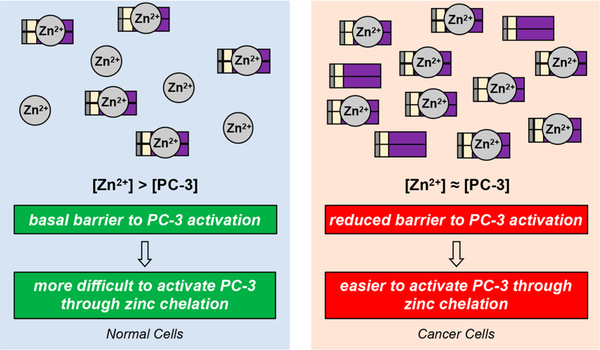
Figure [3]

Figure [4]

Figure [5]
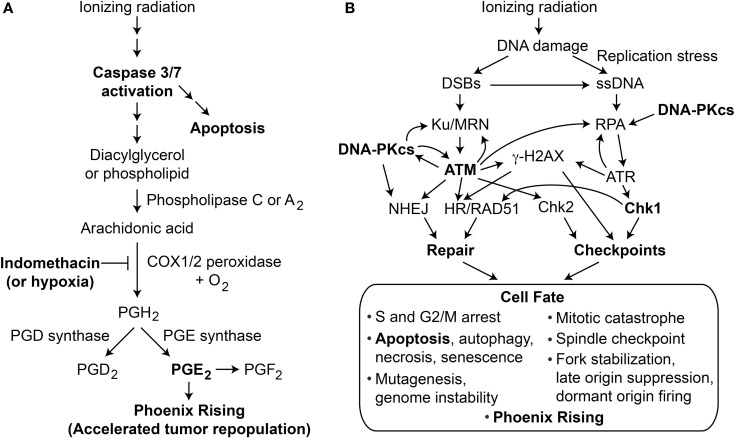
Figure [6]
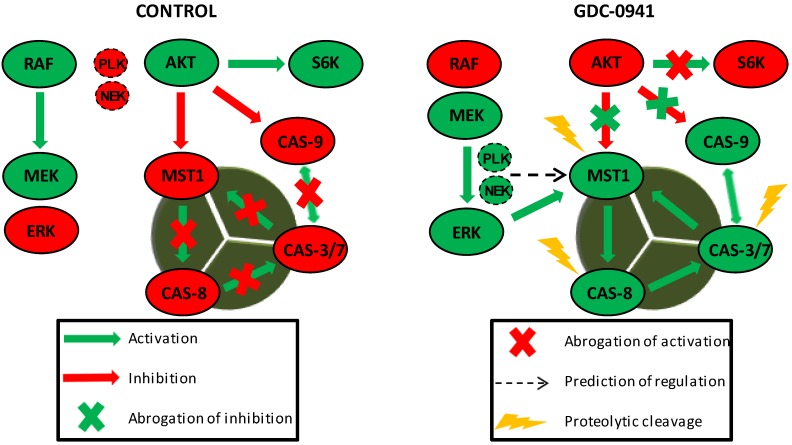
Figure [7]

Figure [8]
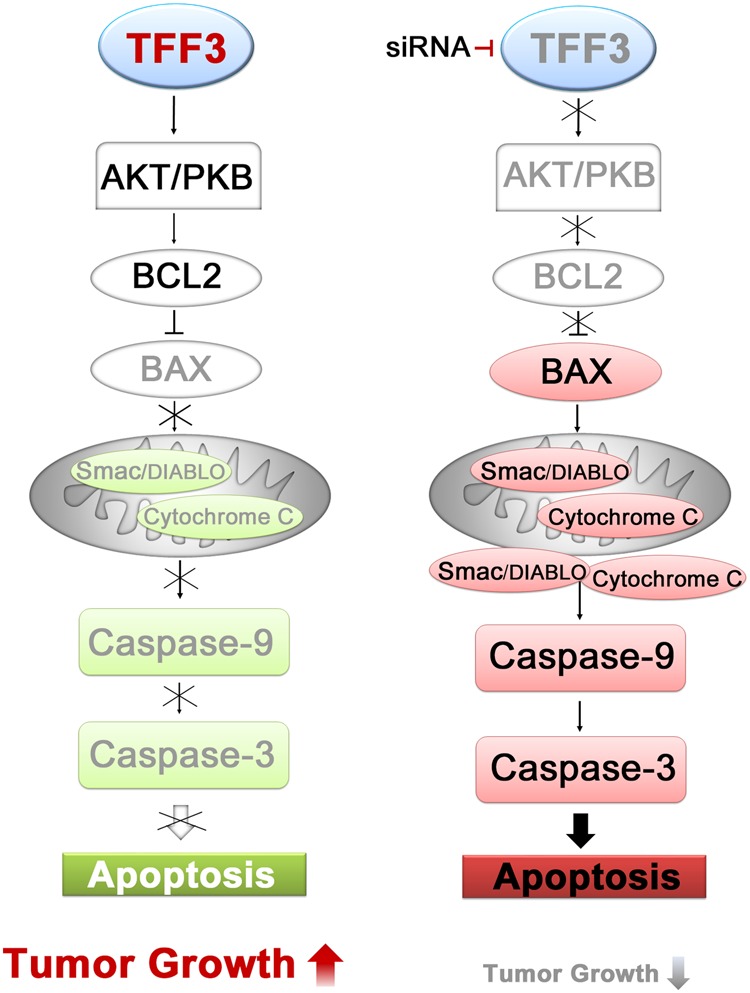
Figure [9]
Note: If you are interested in the full version of this target analysis report, or if you'd like to learn how our AI-powered BDE-Chem can design therapeutic molecules to interact with the CASP3 target at a cost 90% lower than traditional approaches, please feel free to contact us at BD@silexon.ai.
More Common Targets
ABCB1 | ABCG2 | ACE2 | AHR | AKT1 | ALK | AR | ATM | BAX | BCL2 | BCL2L1 | BECN1 | BRAF | BRCA1 | CAMP | CASP3 | CASP9 | CCL5 | CCND1 | CD274 | CD4 | CD8A | CDH1 | CDKN1A | CDKN2A | CREB1 | CXCL8 | CXCR4 | DNMT1 | EGF | EGFR | EP300 | ERBB2 | EREG | ESR1 | EZH2 | FN1 | FOXO3 | HDAC9 | HGF | HMGB1 | HSP90AA1 | HSPA4 | HSPA5 | IDO1 | IFNA1 | IGF1 | IGF1R | IL17A | IL6 | INS | JUN | KRAS | MAPK1 | MAPK14 | MAPK3 | MAPK8 | MAPT | MCL1 | MDM2 | MET | MMP9 | MTOR | MYC | NFE2L2 | NLRP3 | NOTCH1 | PARP1 | PCNA | PDCD1 | PLK1 | PRKAA1 | PRKAA2 | PTEN | PTGS2 | PTK2 | RELA | SIRT1 | SLTM | SMAD4 | SOD1 | SQSTM1 | SRC | STAT1 | STAT3 | STAT5A | TAK1 | TERT | TLR4 | TNF | TP53 | TXN | VEGFA | YAP1

